Why Monasteries?

Standing Male Worshipper, c. 2900-2600 B.C.E., Metropolitan Museum of Art
Standing Male Worshipper (votive figure), c. 2900-2600 B.C.E., Eshnunna (modern Tell Asmar, Iraq), gypsum alabaster, shell, black limestone, bitumen, 11 5/8 x 5 1/8 x 3 7/8″ / 29.5 x 10 cm, Sumerian (The Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York City)
What is a monastery exactly? A monastery is a community of men or women (monks or nuns), who have chosen to withdraw from society, forming a new community devoted to religious practice. The word monk comes from the Greek word monos, which means alone.
It can be difficult to focus a lot of time on prayers and religious ritual when time needs to be spent on everyday activities that insure one’s survival (such as food and shelter). Think of the ancient Sumerian Votive Statues from Tell Asmar, for example (image, left). These statues were placed in a temple high above the village. Each statue represented an individual in continual prayer as a stand-in for the actual individual who was busy living, tending to crops, cooking food, and raising children. The person was depicted with hands clasped in prayer (at the heart center) with eyes wide open in perpetual engagement with the gods.
The work of the monastery
In Buddhism and Christianity however, instead of statues, monks or nuns pray on behalf of the people. The monastery typically becomes the spiritual focus of the nearest town or village. In Christianity the monks pray for the salvation of the souls of the living. But in Buddhism, there is no concept of the soul. The goal is not heaven, rather it is cessation from the endless cycle of rebirth (samsara), to achieve moksha, which is freedom or release from attachment to ego or the material world and an end to samsara, and to realize nirvana (or liberation), which is to be released into the infinite state of oneness with everything.
The Four Noble Truths or Dharma
It is difficult to achieve moksha, which is why the Buddha’s teaching focuses on achieving Enlightenment or knowledge that helps the practitioner. This is described succinctly in his Four Noble Truths, also referred to as the dharma (the law):
Life is suffering (suffering = rebirth)
The cause of suffering is desire
The cause of desire must be overcome
When desire is overcome, there is no more suffering (suffering = rebirth)
Adept practitioners of Buddhism understood that not everyone was ready to perform the necessary rites to obtain the ultimate goals of ending samsara (rebirth). The common person could, however, improve their karma (an action or deed that enacts a cycle of cause and effect) by everyday charitable acts that were mostly directed toward the monastic community.
The Buddhist monks and nuns meditated and prayed on behalf of the lay community (or laity—basically everyone who is not a priest or monk), those without specialized knowledge of the faith, assisting them in the goal of realizing The Four Noble Truths. Monks and nuns also instructed the lay practitioner on how to conduct the rituals, how to meditate, and advised them about which Buddhist deity to focus on (this depended on the issue or obstacle in the practitioner’s path to Enlightenment). The laity, in turn, supported the monks with donations of food and other necessary items. It was a mutually beneficial relationship.
The beginnings of monasteries
In the early years of Buddhism, following the practices of contemporary religions such as Hinduism and Jainism (and other faiths that no longer exist), monks dedicated themselves to an ascetic life (a practice of self-denial particular to the pursuit of religious or spiritual goals) wandering the country with no permanent living quarters. They were fed, clothed, and housed in inclement weather by people wishing to gain merit, which is a spiritual credit earned through virtuous acts. Eventually monastic complexes were created for the monks close enough to a town in order to receive alms or charity from the villagers, but far enough away so as not to be disturbed during meditation.
Three types of architecture: stupa, vihara and the chaitya
Buddhism, the first Indian religion to require large communal and monastic spaces, inspired three types of architecture.
The first was the stupa, a significant object in Buddhist art and architecture. On a very basic level it is a burial mound for the Buddha. The original stupas contained the Buddha's ashes. Relics are objects associated with an esteemed person, including that person’s bones (or ashes in the case of the Buddha), or things the person used or had worn. The veneration, or respect, for relics is prevalent in many religious faiths, particularly in Christianity. By the time the Buddhist monasteries gained importance, the stupas were empty of these relics and simply became symbols of the Buddha and the Buddhist ideology.
Second was the construction of the vihara, a Buddhist monastery that also contained a residence hall for the monks.
Third was the chaitya, an assembly hall that contained a stupa (though one empty of relics). This became an important feature for the monasteries that were cut into cliffs in central India. The central hall of the chaitya was arranged to allow for circumambulation of the stupa.
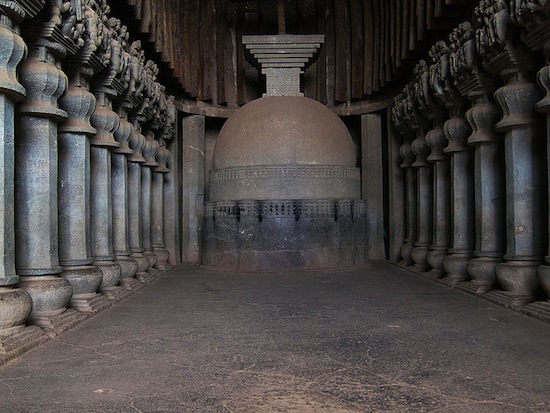

Chaitya at Karle near Lonavala, Maharashtra, first century B.C.E
Chaitya at Karle near Lonavala, Maharashtra, first century B.C.E., photo: //www.flickr.com/photos/82289802@N00/8233109522">Fernando Stankuns (CC BY-NC-SA 2.0)
The stupa is at the end of the nave (the main central aisle), as seen in the photo above. On either side of the columns are side aisles to help people walk through the space—around to the stupa, and back out. This is similar to the architecture of Early Christianity (for example, the side aisles at the Early Christian Church in Rome, Santa Sabina, which help the flow of people who come to worship at the altar at the end of the nave).
Buddhist Monasteries in India
In India, by the 1st century, many monasteries were founded as learning centers on sites already associated with Buddha and Buddhism. These sites include Lumbini where the Buddha was born, Bodh Gaya where he achieved enlightenment and the knowledge of the dharma (the Four Noble Truths), Sarnath (Deer Park) where he preached his first sermon sharing the dharma, and Kushingara where he died.
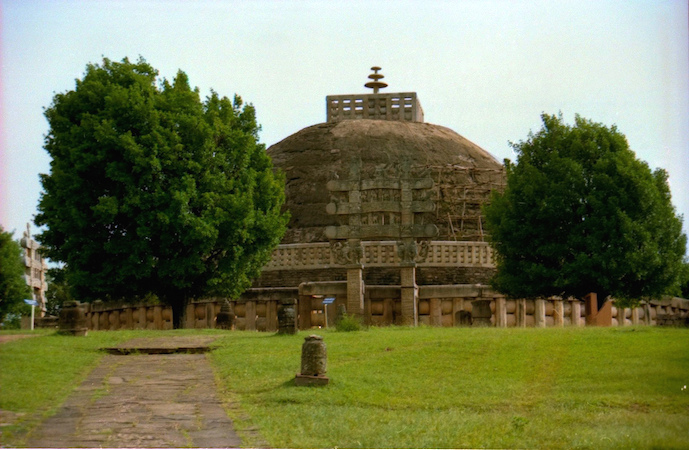

Great Stupa, Sanchi, India, 3rd century B.C.E. to first century C.E., photo: R Barraez D´Lucca (CC BY 2.0)
Great Stupa, Sanchi, India, 3rd century B.C.E. to first century C.E., photo: R Barraez D´Lucca (CC BY 2.0)
Ashoka: the first King to embrace Buddhism
Sites special to King Ashoka (304–232 B.C.E.), the first king (of northern India) to embrace Buddhism, were also integral to the building of monasteries. For example, the complex at Sanchi, where the original Great Stupa (Mahastupa) of Sanchi was created as a reliquary for the Buddha’s ashes after his death, became the largest of many stupas that were created later when a monastery was built at the site. Ashoka added one of his famous pillars at this location—pillars that not only proclaimed his acceptance of Buddhism, but also served as instructional objects on Buddhist ideology.
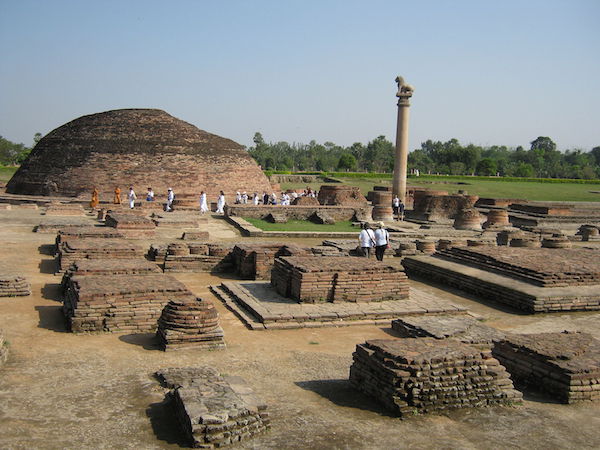

An example of the monastic center at Vaishali, one can still see the remains of one of several stupas, the Ashokan pillar and the later addition of the monks’ cells and the administrative center, photo: Abhishek Singh
An example of the monastic center at Vaishali, one can still see the remains of one of several stupas, the Ashokan pillar and the later addition of the monks’ cells and the administrative center. Soon these types of monasteries were replaced by rock-cut accommodations due to their durability, photo: Abhishek Singh (CC BY-SA 3.0)
Between 120 BCE and 200 C.E. over 1000 viharas (a monastery with residence hall for the monks), and chaityas (a stupa monument hall), were established along ancient and prosperous trade routes. The monasteries required large living areas.
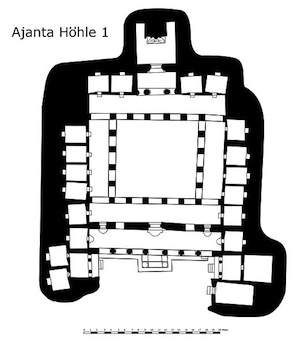
Plan of cave 1 at Ajanta
Plan of cave 1 at Ajanta
A vihara was a dwelling of one or two stories, fronted by a pillared veranda. The monks’ or nuns’ cells were arranged around a central meeting hall as in the plan of the Ajanta vihara (left). Each cell contained a stone bed, a pillow and a niche for a lamp.
The monastery quickly became important and had a three-fold purpose: as a residence for monks, as a center for religious work (on behalf of the laity) and as a center for Buddhist learning. During Ashoka’s reign in the 3rd century B.C.E., the Mahabodhi Temple (the Great Temple of Enlightenment where Buddha achieved his knowledge of the dharma—the Four Noble Truths) was built in Bodh Gaya, currently in the Indian state of Bihar in northern India. It contained a monastery and shrine. In order to acknowledge the exact site where the Buddha attained Enlightenment, Ashoka built a diamond throne (vajrasana - literally diamond seat) underscoring the indestructible path of the dharma.
Rock-cut caves
The rock-cut caves were established in the 3rd century B.C.E. in the western Deccan Plateau, which makes up most of the southern portion of India. The earliest rock-cut monastic centers include the Bhaja Caves, the Karle Caves and the Ajanta Caves.
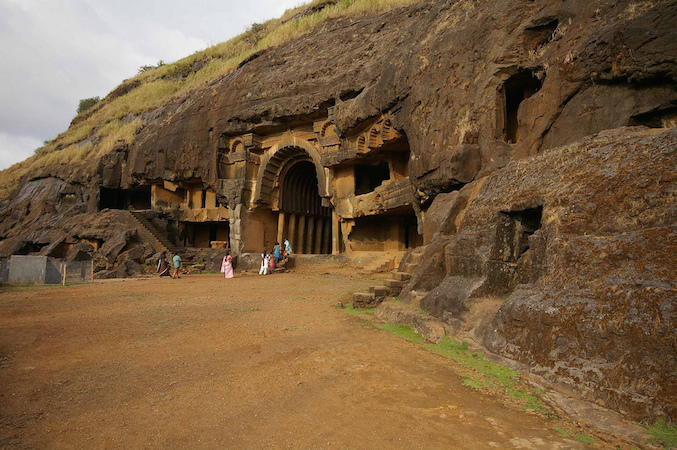

Bhaja Caves, c. 3rd century B.C.E. to 2nd century B.C.E., photo: Andrea Kirkby. Twenty-two caves are located at the site.
Bhaja Caves, c. 3rd century B.C.E. to 2nd century B.C.E., photo: Andrea Kirkby (CC BY-NC 2.0). Twenty-two caves are located at the site.
The objects found in the caves suggest a profitable relationship existed between the monks and wealthy traders. The Bhaja caves were located on a major trade route from the Arabian Sea eastward toward the Deccan region linking north and south India. Merchants, wealthy from the trade between the Roman Empire and southeast Asia, often sponsored architectural additions including pillars, arches, reliefs and façades to the caves. Buddhist monks, serving as missionaries, often accompanied traders throughout India, up into Nepal and Tibet, spreading the dharma as they travelled.
Bhaja

Chaitya (monastic monument hall) at Bhaja, India, 1st century B.C.E. (photo: Andrea Kirkby)
Chaitya (monastic monument hall) at Bhaja, India, 1st century B.C.E., photo: //www.flickr.com/photos/12071889@N00/5427315841">Andrea Kirkby (CC BY-NC 2.0)
At Bhaja there are no representations of the Buddha other than the stupa since Bhaja was an active monastery during the earliest phase of Buddhism, Hinayana (lesser vehicle), when no images of the Buddha were created. In Hinayana, the memory of the historical Buddha and his teachings were still a very real part of the practice. The Buddha himself did not encourage worship of him (something images would encourage), but desired that the practitioner focus on the dharma (the law, the Four Noble Truths).
The main chaitya hall (which contained a memorial stupa, empty of relics, above) at Bhaja contains a solid stone stupa in the nave flanked by two side aisles. It is the earliest example of this type of rock-cut cave and closely resembles the wooden structures that preceded it. The columns slope inwards, which would have been necessary in the early wooden structures in the north of India in order to support the outward thrust from the top of the vault. In similar stone caves, sometimes the columns are placed in stone pots, which mimic the stone pots the wooden columns were positioned in, in order to thwart termites. This is an example of a practical architectural practice being adopted as the standard.

Ajanta, cave 19 (Photo: Arian Zwegers)
Ajanta, cave 19, photo: //www.flickr.com/photos/67769030@N07/6354420107">Arian Zwegers, (CC BY 2.0)
Ajanta
At Ajanta, the earliest phase of construction also belongs to the Hinayana (lesser vehicle) phase of Buddhism (in which no human image of the Buddha was created). The caves are very similar to those at Bhaja. During the second phase of construction, Buddhism was in the Mahayana (greater vehicle) phase and images of the Buddha, predominantly drawn from the jataka stories—the life stories of the Buddha—were painted throughout. In Mahayana, which was more distant in time from the life of the Buddha, there was a need for physical reminders of the Buddha and his teachings. Thus images of the Buddha performing his Enlightenment and his first sermon (when he shared the Four Noble Truths with the laity) proliferated. The paintings at Ajanta provide some of the earliest and finest examples of Buddhist painting from the period. The images also provide documentation of contemporary events and social custom under Gupta reign (320-550 C.E.).
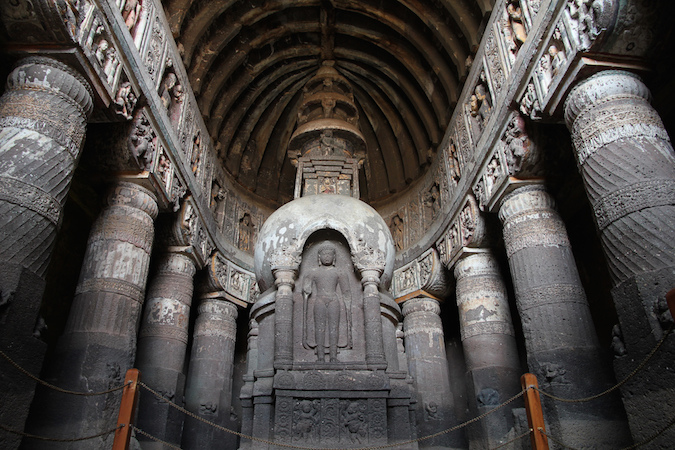

Ajanta, Cave 19 (interior), photo: Kirk Kittell (CC BY-NC 2.0)
Ajanta, Cave 19 (interior), photo: Kirk Kittell (CC BY-NC 2.0)
Rock-cut monasteries become more complex
Eventually, the rock-cut monasteries became quite complex. They consisted of several stories with inner courtyards and veranda. Some facades had reliefs, images projecting from the stone, of the Buddha and other deities. A stupa was still placed in the central hall, but now an image of the Buddha was carved into it, underscoring that the Buddha is the stupa. Stories from the Buddha’s life were also, at times, added to the interior in both paintings and reliefs.
Essay by Dr. Karen Shelby


